You Only Need 90K Parameters to Adapt Light: A Light Weight Transformer for Image Enhancement and Exposure Correction
0. 写在前面
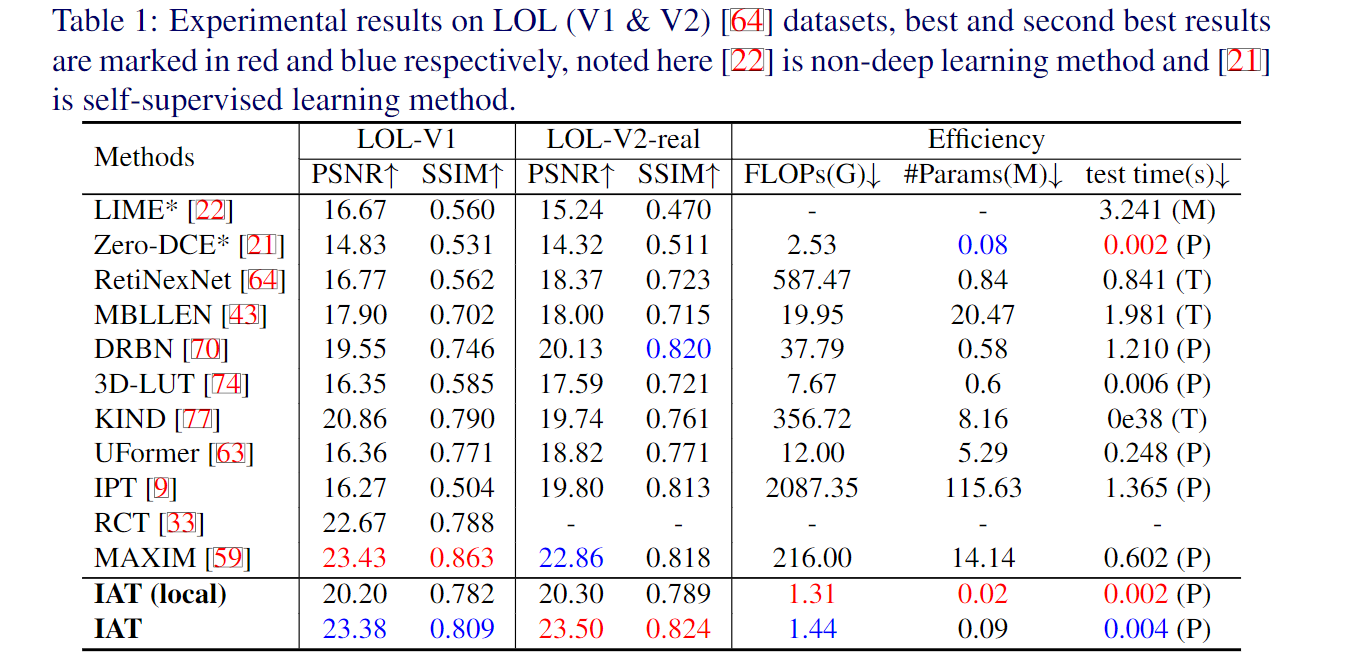
虽然作者说该模型采用了轻量化的设计思想,Params只有90K,但是经过笔者实际测试发现,模型在推理时的FLOAT高达5.5G,因此远远不是实时性运行的算法。
1. 论文基本信息
2. 论文主要内容
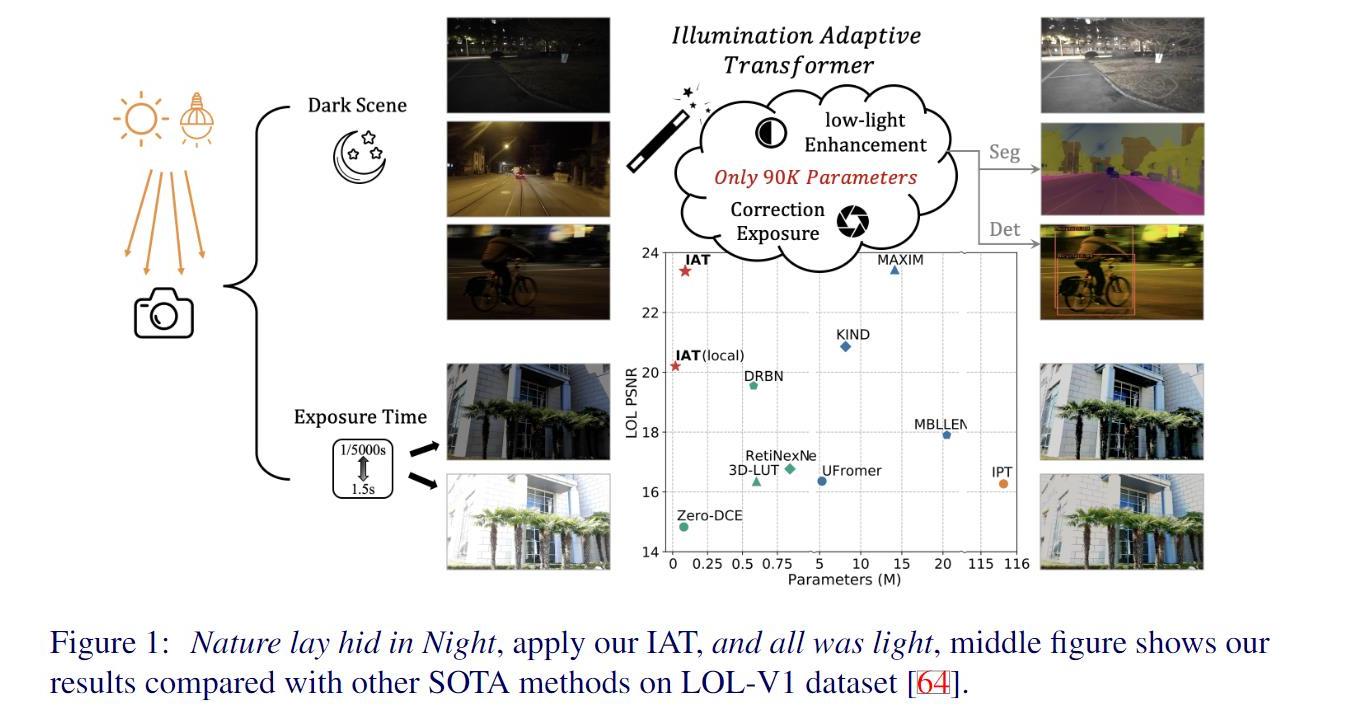
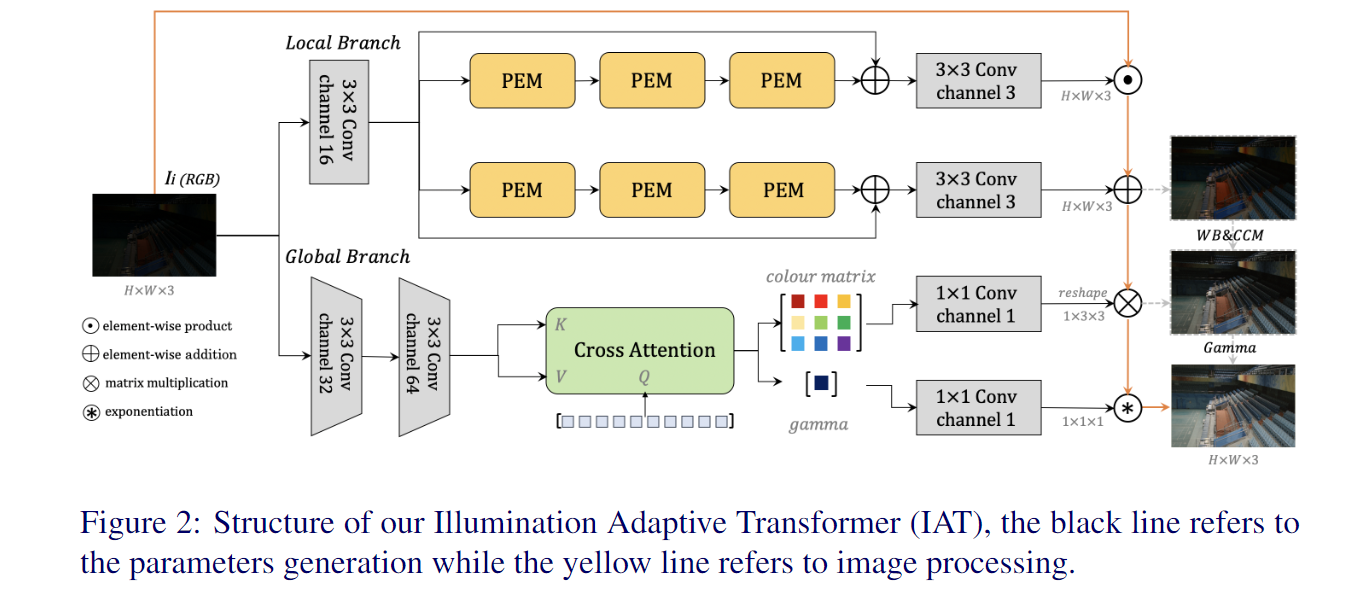
自然场景下存在着各种不良光照场景,如低光照环境和摄影造成的过(欠)曝光环境,相机在不良光照下完成摄影任务时,因为接收到过多/过少的光子数量,和相机内部的处理过程 (如低光照场景需要调高ISO,这会导致噪声也同时放大),往往得到的图像也会收到影响,无论从视觉感观还是完成一些视觉任务(如检测,分割等)都会受到影响。区别于传统的HE或者RetiNex做法以及此前的CNN做法,作者提出了Illimination-Adaptive-Transformer (IAT), IAT模型借鉴了目标检测网络DETR思路,通过动态query学习的机制来调整计算摄影中的一些相关参数,建立了一个end-to-end的Transformer,来克服这些不良光照所造成的视觉感观/视觉任务影响。
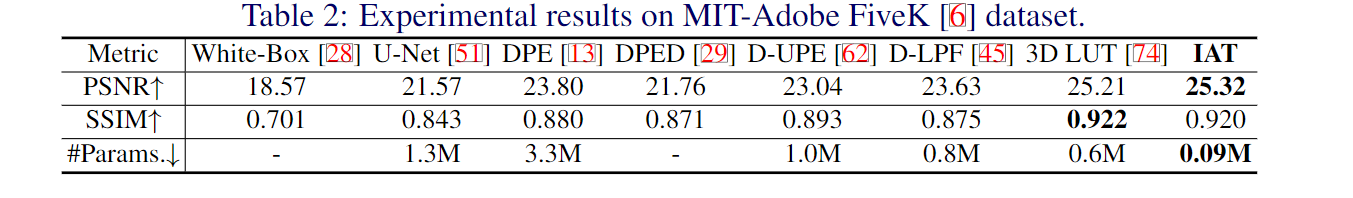
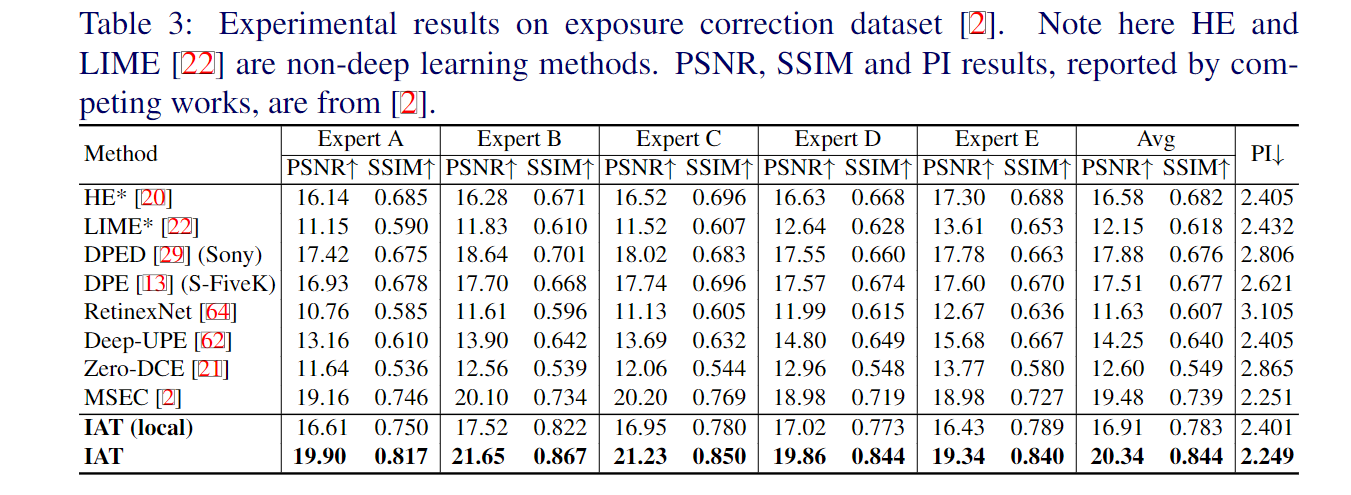
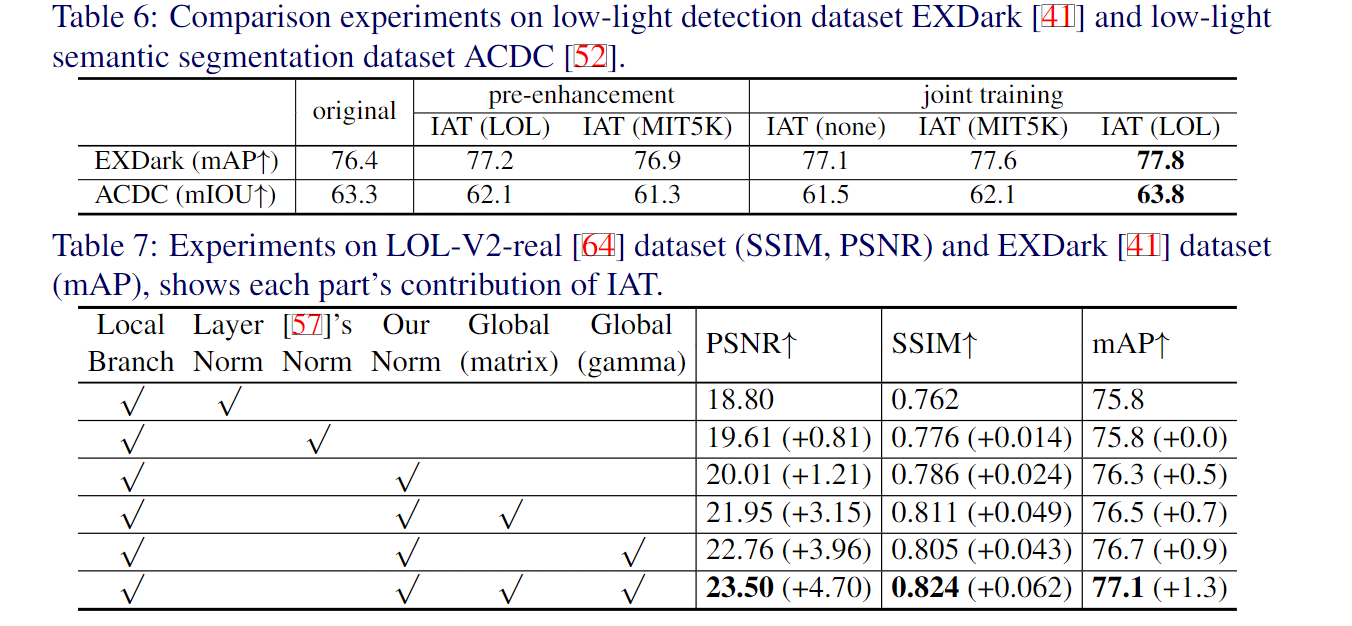
在实验部分,作者做了大量的实验,包括低光照增强/曝光矫正,以及低光照场景下的目标检测,低光照场景下的语义分割,以及复杂光照场景下的目标检测。具体而言,低光照增强用的是LOL-V1和LOL-V2-real数据集;曝光矫正采用的是Exposure数据集。低光照检测/分割方面,作者分别用低光照检测数据集EXDark和低光照分割数据集ACDC以及多光源场景检测数据集TYOL进行验证。检测器采用的是YOLOv3。
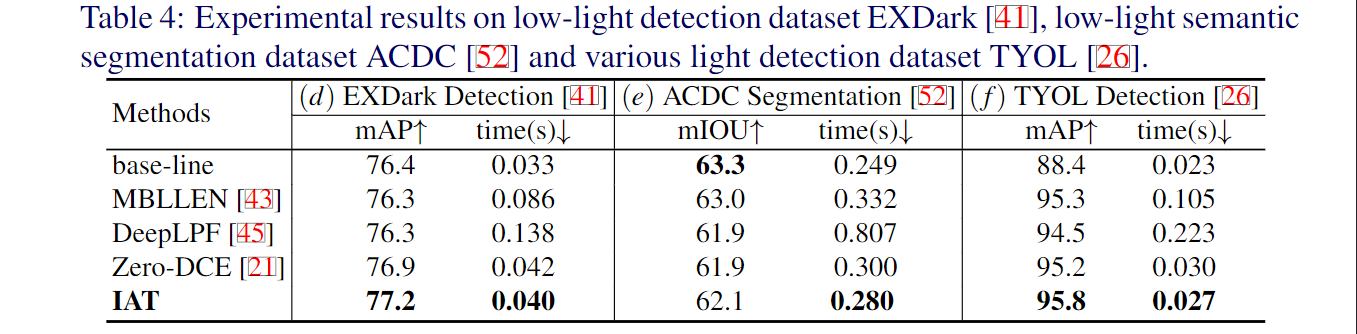
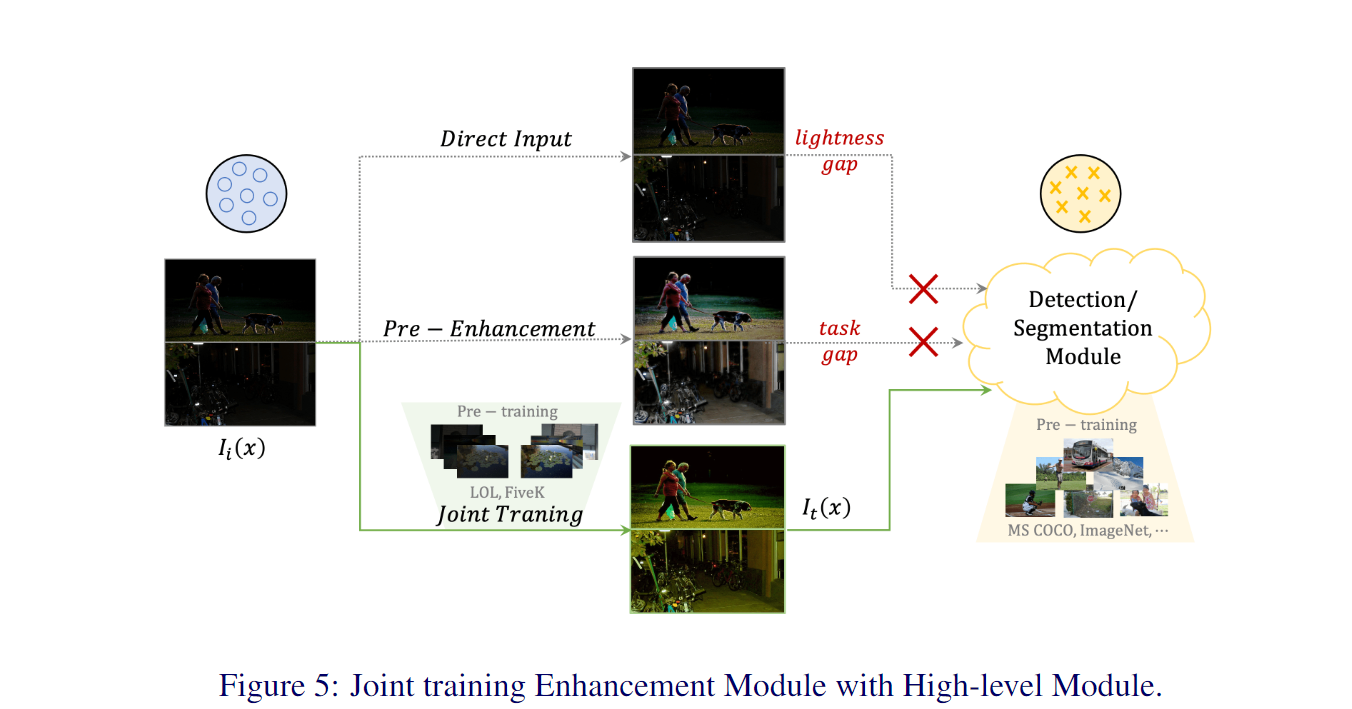
可以看出低光照增强方法对于目标检测任务有些许提升,但是在后续的语义分割任务(e)上,增强算法反而无法提升目标的分割性能,这是由于图像增强算法与高层视觉算法的目的与评价指标不一致所导致的,图像增强是为了更好提升人眼视觉(评价指标PSNR,SSIM),而目标检测和语义分割属于机器视觉(评价指标mIOU, mAP)。
针对于这种情况,作者采用了joint-training范式来训练网络,即将图像增强网络和后续检测分割网络联合,一起更新参数,其中图像增强网络还可以加载不同的预训练模型(如LOL数据集预训练和MIT-5K数据集预训练)。
3. 论文源码解析
3.1 IAT_model.py
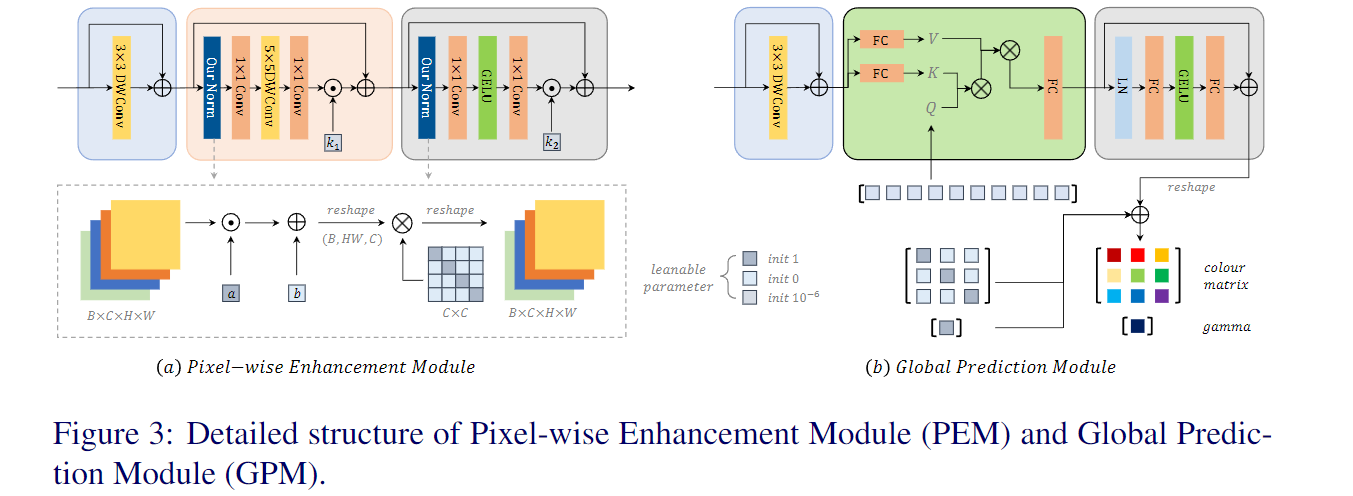
IAT模型除了常规的导入torch、numpy外,还需要额外导入两个作者自己实现的一些模型结构细节,首先是Global_pred其次是CBlock_ln和SwinTransformerBlock。
Global_pred.py
import imp
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from timm.models.layers import trunc_normal_, DropPath, to_2tuple
import os
class Mlp(nn.Module):
# taken from https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/master/timm/models/vision_transformer.py
def __init__(self, in_features, hidden_features=None, out_features=None, act_layer=nn.GELU, drop=0.):
super().__init__()
out_features = out_features or in_features
hidden_features = hidden_features or in_features
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_features, hidden_features)
self.act = act_layer()
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_features, out_features)
self.drop = nn.Dropout(drop)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.act(x)
x = self.drop(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.drop(x)
return x
class query_Attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, num_heads=2, qkv_bias=False, qk_scale=None, attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0.):
super().__init__()
self.num_heads = num_heads
head_dim = dim // num_heads
# NOTE scale factor was wrong in my original version, can set manually to be compat with prev weights
self.scale = qk_scale or head_dim ** -0.5
self.q = nn.Parameter(torch.ones((1, 10, dim)), requires_grad=True)
self.k = nn.Linear(dim, dim, bias=qkv_bias)
self.v = nn.Linear(dim, dim, bias=qkv_bias)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)
def forward(self, x):
B, N, C = x.shape
k = self.k(x).reshape(B, N, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads).permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
v = self.v(x).reshape(B, N, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads).permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
q = self.q.expand(B, -1, -1).view(B, -1, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads).permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)) * self.scale
attn = attn.softmax(dim=-1)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
x = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B, 10, C)
x = self.proj(x)
x = self.proj_drop(x)
return x
class query_SABlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, num_heads, mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=False, qk_scale=None, drop=0., attn_drop=0.,
drop_path=0., act_layer=nn.GELU, norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm):
super().__init__()
self.pos_embed = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 3, padding=1, groups=dim)
self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim)
self.attn = query_Attention(
dim,
num_heads=num_heads, qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale,
attn_drop=attn_drop, proj_drop=drop)
# NOTE: drop path for stochastic depth, we shall see if this is better than dropout here
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()
self.norm2 = norm_layer(dim)
mlp_hidden_dim = int(dim * mlp_ratio)
self.mlp = Mlp(in_features=dim, hidden_features=mlp_hidden_dim, act_layer=act_layer, drop=drop)
def forward(self, x):
x = x + self.pos_embed(x)
x = x.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2)
x = self.drop_path(self.attn(self.norm1(x)))
x = x + self.drop_path(self.mlp(self.norm2(x)))
return x
class conv_embedding(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super(conv_embedding, self).__init__()
self.proj = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels // 2, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels // 2),
nn.GELU(),
# nn.Conv2d(out_channels // 2, out_channels // 2, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1)),
# nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels // 2),
# nn.GELU(),
nn.Conv2d(out_channels // 2, out_channels, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1)),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.proj(x)
return x
class Global_pred(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels=3, out_channels=64, num_heads=4, type='exp'):
super(Global_pred, self).__init__()
if type == 'exp':
self.gamma_base = nn.Parameter(torch.ones((1)), requires_grad=False) # False in exposure correction
else:
self.gamma_base = nn.Parameter(torch.ones((1)), requires_grad=True)
self.color_base = nn.Parameter(torch.eye((3)), requires_grad=True) # basic color matrix
# main blocks
self.conv_large = conv_embedding(in_channels, out_channels)
self.generator = query_SABlock(dim=out_channels, num_heads=num_heads)
self.gamma_linear = nn.Linear(out_channels, 1)
self.color_linear = nn.Linear(out_channels, 1)
self.apply(self._init_weights)
for name, p in self.named_parameters():
if name == 'generator.attn.v.weight':
nn.init.constant_(p, 0)
def _init_weights(self, m):
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
trunc_normal_(m.weight, std=.02)
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear) and m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.LayerNorm):
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1.0)
def forward(self, x):
#print(self.gamma_base)
x = self.conv_large(x)
x = self.generator(x)
gamma, color = x[:, 0].unsqueeze(1), x[:, 1:]
gamma = self.gamma_linear(gamma).squeeze(-1) + self.gamma_base
#print(self.gamma_base, self.gamma_linear(gamma))
color = self.color_linear(color).squeeze(-1).view(-1, 3, 3) + self.color_base
return gamma, color
if __name__ == "__main__":
os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES']='3'
#net = Local_pred_new().cuda()
img = torch.Tensor(8, 3, 400, 600)
global_net = Global_pred()
gamma, color = global_net(img)
print(gamma.shape, color.shape)blocks.py
"""
Code copy from uniformer source code:
https://github.com/Sense-X/UniFormer
"""
import os
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from functools import partial
import math
from timm.models.vision_transformer import VisionTransformer, _cfg
from timm.models.registry import register_model
from timm.models.layers import trunc_normal_, DropPath, to_2tuple
# ResMLP's normalization
class Aff(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim):
super().__init__()
# learnable
self.alpha = nn.Parameter(torch.ones([1, 1, dim]))
self.beta = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros([1, 1, dim]))
def forward(self, x):
x = x * self.alpha + self.beta
return x
# Color Normalization
class Aff_channel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, channel_first = True):
super().__init__()
# learnable
self.alpha = nn.Parameter(torch.ones([1, 1, dim]))
self.beta = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros([1, 1, dim]))
self.color = nn.Parameter(torch.eye(dim))
self.channel_first = channel_first
def forward(self, x):
if self.channel_first:
x1 = torch.tensordot(x, self.color, dims=[[-1], [-1]])
x2 = x1 * self.alpha + self.beta
else:
x1 = x * self.alpha + self.beta
x2 = torch.tensordot(x1, self.color, dims=[[-1], [-1]])
return x2
class Mlp(nn.Module):
# taken from https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/master/timm/models/vision_transformer.py
def __init__(self, in_features, hidden_features=None, out_features=None, act_layer=nn.GELU, drop=0.):
super().__init__()
out_features = out_features or in_features
hidden_features = hidden_features or in_features
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_features, hidden_features)
self.act = act_layer()
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_features, out_features)
self.drop = nn.Dropout(drop)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.act(x)
x = self.drop(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.drop(x)
return x
class CMlp(nn.Module):
# taken from https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/master/timm/models/vision_transformer.py
def __init__(self, in_features, hidden_features=None, out_features=None, act_layer=nn.GELU, drop=0.):
super().__init__()
out_features = out_features or in_features
hidden_features = hidden_features or in_features
self.fc1 = nn.Conv2d(in_features, hidden_features, 1)
self.act = act_layer()
self.fc2 = nn.Conv2d(hidden_features, out_features, 1)
self.drop = nn.Dropout(drop)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.act(x)
x = self.drop(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.drop(x)
return x
class CBlock_ln(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=False, qk_scale=None, drop=0., attn_drop=0.,
drop_path=0., act_layer=nn.GELU, norm_layer=Aff_channel, init_values=1e-4):
super().__init__()
self.pos_embed = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 3, padding=1, groups=dim)
#self.norm1 = Aff_channel(dim)
self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 1)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 1)
self.attn = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 5, padding=2, groups=dim)
# NOTE: drop path for stochastic depth, we shall see if this is better than dropout here
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()
#self.norm2 = Aff_channel(dim)
self.norm2 = norm_layer(dim)
mlp_hidden_dim = int(dim * mlp_ratio)
self.gamma_1 = nn.Parameter(init_values * torch.ones((1, dim, 1, 1)), requires_grad=True)
self.gamma_2 = nn.Parameter(init_values * torch.ones((1, dim, 1, 1)), requires_grad=True)
self.mlp = CMlp(in_features=dim, hidden_features=mlp_hidden_dim, act_layer=act_layer, drop=drop)
def forward(self, x):
x = x + self.pos_embed(x)
B, C, H, W = x.shape
#print(x.shape)
norm_x = x.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2)
#print(norm_x.shape)
norm_x = self.norm1(norm_x)
norm_x = norm_x.view(B, H, W, C).permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
x = x + self.drop_path(self.gamma_1*self.conv2(self.attn(self.conv1(norm_x))))
norm_x = x.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2)
norm_x = self.norm2(norm_x)
norm_x = norm_x.view(B, H, W, C).permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
x = x + self.drop_path(self.gamma_2*self.mlp(norm_x))
return x
def window_partition(x, window_size):
"""
Args:
x: (B, H, W, C)
window_size (int): window size
Returns:
windows: (num_windows*B, window_size, window_size, C)
"""
B, H, W, C = x.shape
#print(x.shape)
x = x.view(B, H // window_size, window_size, W // window_size, window_size, C)
windows = x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5).contiguous().view(-1, window_size, window_size, C)
return windows
def window_reverse(windows, window_size, H, W):
"""
Args:
windows: (num_windows*B, window_size, window_size, C)
window_size (int): Window size
H (int): Height of image
W (int): Width of image
Returns:
x: (B, H, W, C)
"""
B = int(windows.shape[0] / (H * W / window_size / window_size))
x = windows.view(B, H // window_size, W // window_size, window_size, window_size, -1)
x = x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5).contiguous().view(B, H, W, -1)
return x
class WindowAttention(nn.Module):
r""" Window based multi-head self attention (W-MSA) module with relative position bias.
It supports both of shifted and non-shifted window.
Args:
dim (int): Number of input channels.
window_size (tuple[int]): The height and width of the window.
num_heads (int): Number of attention heads.
qkv_bias (bool, optional): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: True
qk_scale (float | None, optional): Override default qk scale of head_dim ** -0.5 if set
attn_drop (float, optional): Dropout ratio of attention weight. Default: 0.0
proj_drop (float, optional): Dropout ratio of output. Default: 0.0
"""
def __init__(self, dim, window_size, num_heads, qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None, attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0.):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.window_size = window_size # Wh, Ww
self.num_heads = num_heads
head_dim = dim // num_heads
self.scale = qk_scale or head_dim ** -0.5
self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3, bias=qkv_bias)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
def forward(self, x):
B_, N, C = x.shape
qkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(B_, N, 3, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads).permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4)
q, k, v = qkv[0], qkv[1], qkv[2] # make torchscript happy (cannot use tensor as tuple)
q = q * self.scale
attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1))
attn = self.softmax(attn)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
x = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B_, N, C)
x = self.proj(x)
x = self.proj_drop(x)
return x
## Layer_norm, Aff_norm, Aff_channel_norm
class SwinTransformerBlock(nn.Module):
r""" Swin Transformer Block.
Args:
dim (int): Number of input channels.
input_resolution (tuple[int]): Input resulotion.
num_heads (int): Number of attention heads.
window_size (int): Window size.
shift_size (int): Shift size for SW-MSA.
mlp_ratio (float): Ratio of mlp hidden dim to embedding dim.
qkv_bias (bool, optional): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: True
qk_scale (float | None, optional): Override default qk scale of head_dim ** -0.5 if set.
drop (float, optional): Dropout rate. Default: 0.0
attn_drop (float, optional): Attention dropout rate. Default: 0.0
drop_path (float, optional): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.0
act_layer (nn.Module, optional): Activation layer. Default: nn.GELU
norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): Normalization layer. Default: nn.LayerNorm
"""
def __init__(self, dim, num_heads=2, window_size=8, shift_size=0,
mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None, drop=0., attn_drop=0., drop_path=0.,
act_layer=nn.GELU, norm_layer=Aff_channel):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.window_size = window_size
self.shift_size = shift_size
self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio
self.pos_embed = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 3, padding=1, groups=dim)
#self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim)
self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim)
self.attn = WindowAttention(
dim, window_size=to_2tuple(self.window_size), num_heads=num_heads,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale, attn_drop=attn_drop, proj_drop=drop)
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()
#self.norm2 = norm_layer(dim)
self.norm2 = norm_layer(dim)
mlp_hidden_dim = int(dim * mlp_ratio)
self.mlp = Mlp(in_features=dim, hidden_features=mlp_hidden_dim, act_layer=act_layer, drop=drop)
def forward(self, x):
x = x + self.pos_embed(x)
B, C, H, W = x.shape
x = x.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2)
shortcut = x
x = self.norm1(x)
x = x.view(B, H, W, C)
# cyclic shift
if self.shift_size > 0:
shifted_x = torch.roll(x, shifts=(-self.shift_size, -self.shift_size), dims=(1, 2))
else:
shifted_x = x
# partition windows
x_windows = window_partition(shifted_x, self.window_size) # nW*B, window_size, window_size, C
x_windows = x_windows.view(-1, self.window_size * self.window_size, C) # nW*B, window_size*window_size, C
# W-MSA/SW-MSA
attn_windows = self.attn(x_windows) # nW*B, window_size*window_size, C
# merge windows
attn_windows = attn_windows.view(-1, self.window_size, self.window_size, C)
shifted_x = window_reverse(attn_windows, self.window_size, H, W) # B H' W' C
x = shifted_x
x = x.view(B, H * W, C)
# FFN
x = shortcut + self.drop_path(x)
x = x + self.drop_path(self.mlp(self.norm2(x)))
x = x.transpose(1, 2).reshape(B, C, H, W)
return x
if __name__ == "__main__":
os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES']='1'
cb_blovk = CBlock_ln(dim = 16)
x = torch.Tensor(1, 16, 400, 600)
swin = SwinTransformerBlock(dim=16, num_heads=4)
x = cb_blovk(x)
print(x.shape)IAT_main.py
import torch
import numpy as np
from torch import nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import os
import math
from timm.models.layers import trunc_normal_
from blocks import CBlock_ln, SwinTransformerBlock
from global_net import Global_pred
from thop import clever_format
from thop import profile
class Local_pred(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim=16, number=4, type='ccc'):
super(Local_pred, self).__init__()
# initial convolution
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, dim, 3, padding=1, groups=1)
self.relu = nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True)
# main blocks
block = CBlock_ln(dim)
block_t = SwinTransformerBlock(dim) # head number
if type =='ccc':
#blocks1, blocks2 = [block for _ in range(number)], [block for _ in range(number)]
blocks1 = [CBlock_ln(16, drop_path=0.01), CBlock_ln(16, drop_path=0.05), CBlock_ln(16, drop_path=0.1)]
blocks2 = [CBlock_ln(16, drop_path=0.01), CBlock_ln(16, drop_path=0.05), CBlock_ln(16, drop_path=0.1)]
elif type =='ttt':
blocks1, blocks2 = [block_t for _ in range(number)], [block_t for _ in range(number)]
elif type =='cct':
blocks1, blocks2 = [block, block, block_t], [block, block, block_t]
# block1 = [CBlock_ln(16), nn.Conv2d(16,24,3,1,1)]
self.mul_blocks = nn.Sequential(*blocks1, nn.Conv2d(dim, 3, 3, 1, 1), nn.ReLU())
self.add_blocks = nn.Sequential(*blocks2, nn.Conv2d(dim, 3, 3, 1, 1), nn.Tanh())
def forward(self, img):
img1 = self.relu(self.conv1(img))
mul = self.mul_blocks(img1)
add = self.add_blocks(img1)
return mul, add
# Short Cut Connection on Final Layer
class Local_pred_S(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_dim=3, dim=16, number=4, type='ccc'):
super(Local_pred_S, self).__init__()
# initial convolution
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_dim, dim, 3, padding=1, groups=1)
self.relu = nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True)
# main blocks
block = CBlock_ln(dim)
block_t = SwinTransformerBlock(dim) # head number
if type =='ccc':
blocks1 = [CBlock_ln(16, drop_path=0.01), CBlock_ln(16, drop_path=0.05), CBlock_ln(16, drop_path=0.1)]
blocks2 = [CBlock_ln(16, drop_path=0.01), CBlock_ln(16, drop_path=0.05), CBlock_ln(16, drop_path=0.1)]
elif type =='ttt':
blocks1, blocks2 = [block_t for _ in range(number)], [block_t for _ in range(number)]
elif type =='cct':
blocks1, blocks2 = [block, block, block_t], [block, block, block_t]
# block1 = [CBlock_ln(16), nn.Conv2d(16,24,3,1,1)]
self.mul_blocks = nn.Sequential(*blocks1)
self.add_blocks = nn.Sequential(*blocks2)
self.mul_end = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(dim, 3, 3, 1, 1), nn.ReLU())
self.add_end = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(dim, 3, 3, 1, 1), nn.Tanh())
self.apply(self._init_weights)
def _init_weights(self, m):
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
trunc_normal_(m.weight, std=.02)
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear) and m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.LayerNorm):
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1.0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
fan_out = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
fan_out //= m.groups
m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2.0 / fan_out))
if m.bias is not None:
m.bias.data.zero_()
def forward(self, img):
img1 = self.relu(self.conv1(img))
# short cut connection
mul = self.mul_blocks(img1) + img1
add = self.add_blocks(img1) + img1
mul = self.mul_end(mul)
add = self.add_end(add)
return mul, add
class IAT(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_dim=3, with_global=True, type='lol'):
super(IAT, self).__init__()
#self.local_net = Local_pred()
self.local_net = Local_pred_S(in_dim=in_dim)
self.with_global = with_global
if self.with_global:
self.global_net = Global_pred(in_channels=in_dim, type=type)
def apply_color(self, image, ccm):
shape = image.shape
image = image.view(-1, 3)
image = torch.tensordot(image, ccm, dims=[[-1], [-1]])
image = image.view(shape)
return torch.clamp(image, 1e-8, 1.0)
def forward(self, img_low):
#print(self.with_global)
mul, add = self.local_net(img_low)
img_high = (img_low.mul(mul)).add(add)
if not self.with_global:
return mul, add, img_high
else:
gamma, color = self.global_net(img_low)
b = img_high.shape[0]
img_high = img_high.permute(0, 2, 3, 1) # (B,C,H,W) -- (B,H,W,C)
img_high = torch.stack([self.apply_color(img_high[i,:,:,:], color[i,:,:])**gamma[i,:] for i in range(b)], dim=0)
img_high = img_high.permute(0, 3, 1, 2) # (B,H,W,C) -- (B,C,H,W)
return mul, add, img_high
if __name__ == "__main__":
os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES']='3'
img = torch.Tensor(1, 3, 400, 600)
net = IAT()
print('total parameters:', sum(param.numel() for param in net.parameters()))
_, _, high = net(img)
print(high.shape)
# 测算模型的float与Params
flops, params = profile(net, inputs=(img, ))
flops, params = clever_format([flops, params], "%.3f")
print(flops, params)3.2 检测/分割脚本
如作者在论文中阐述的,预训练的IAT作为弱光图像预处理然后进行检测/分割的效果不好,联合训练的方式是IAT和检测/分割模型都采用预训练的模型,然后再进行检测/分割任务的二次训练,同步更新IAT与检测/分割模型的参数。联合训练的具体添加方式如下:
_, _, x = IAT_model(img)
x = task_backbone(x)
output = task_head(x)
